Cut out a geographic subset
crop.RdCut out a part of a SpatRaster or SpatVector.
You can crop a SpatRaster with a SpatExtent, or with another object from which an extent can be obtained. Note that the SpatRaster returned may not have the exactly the same extent as the SpatExtent supplied because you can only select entire cells (rows and columns), and you cannot add new areas. See methods like resample and disagg to force SpatRasters to align and extend to add rows and/or columns.
You can only crop rectangular areas of a SpatRaster, but see argument mask=TRUE for setting cell values within SpatRaster to NA; or use the mask method after crop for additional masking options.
You can crop a SpatVector with another SpatVector. If these are not polygons, the minimum convex hull is used. Unlike with intersect the geometries and attributes of y are not transferred to the output. You can also crop a SpatVector with a rectangle (SpatRaster, SpatExtent).
Usage
# S4 method for class 'SpatRaster'
crop(x, y, snap="near", mask=FALSE, touches=TRUE, extend=FALSE, filename="", ...)
# S4 method for class 'SpatRasterDataset'
crop(x, y, snap="near", extend=FALSE)
# S4 method for class 'SpatRasterCollection'
crop(x, y, snap="near", extend=FALSE)
# S4 method for class 'SpatVector'
crop(x, y, ext=FALSE)
# S4 method for class 'SpatGraticule'
crop(x, y)Arguments
- x
SpatRaster or SpatVector
- y
SpatRaster, SpatVector, SpatExtent, or any other object that has a SpatExtent (
extreturns aSpatExtent)- snap
character. One of "near", "in", or "out". Used to align
yto the geometry ofx- mask
logical. Should
ybe used to mask? Only used ifyis a SpatVector, SpatRaster or sf- touches
logical. If
TRUEandmask=TRUE, all cells touched by lines or polygons will be masked, not just those on the line render path, or whose center point is within the polygon- extend
logical. Should rows and/or columns be added if
yis beyond the extent ofx? Also seeextend- filename
character. Output filename
- ...
additional arguments for writing files as in
writeRaster- ext
logical. Use the extent of
yinstead ofy. This also changes the behavior whenyis an extent in two ways: (1) points that are on the extent boundary are removed and (2) lon/lat extents that go beyond -180 or 180 degrees longitude are wrapped around the earth to include areas at the other end of the dateline
Examples
r <- rast(xmin=0, xmax=10, ymin=0, ymax=10, nrows=25, ncols=25)
values(r) <- 1:ncell(r)
e <- ext(-5, 5, -5, 5)
rc <- crop(r, e)
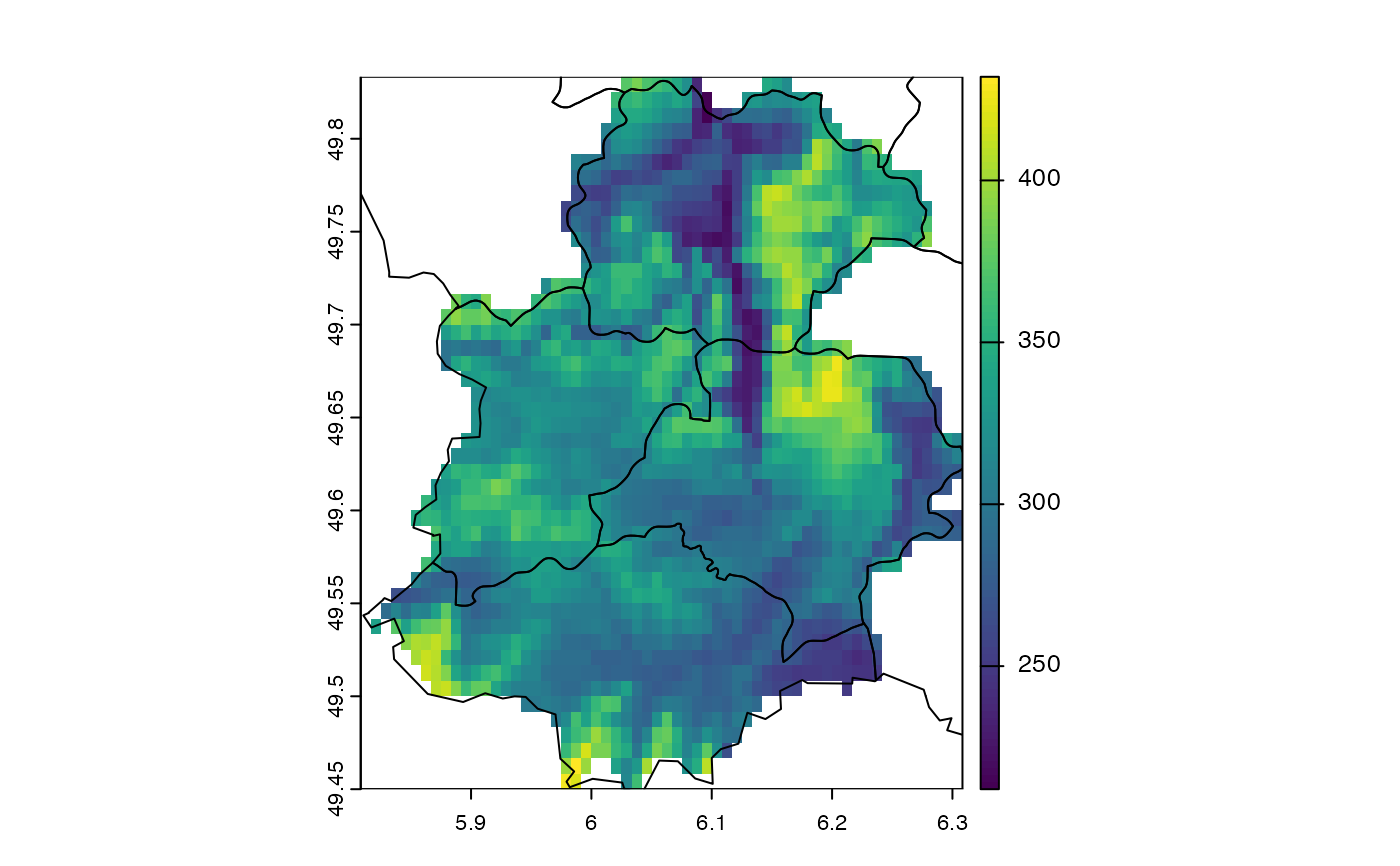
# crop and mask
f <- system.file("ex/elev.tif", package="terra")
r <- rast(f)
f <- system.file("ex/lux.shp", package="terra")
v <- vect(f)
cm <- crop(r, v[9:12,], mask=TRUE)
plot(cm)
lines(v)
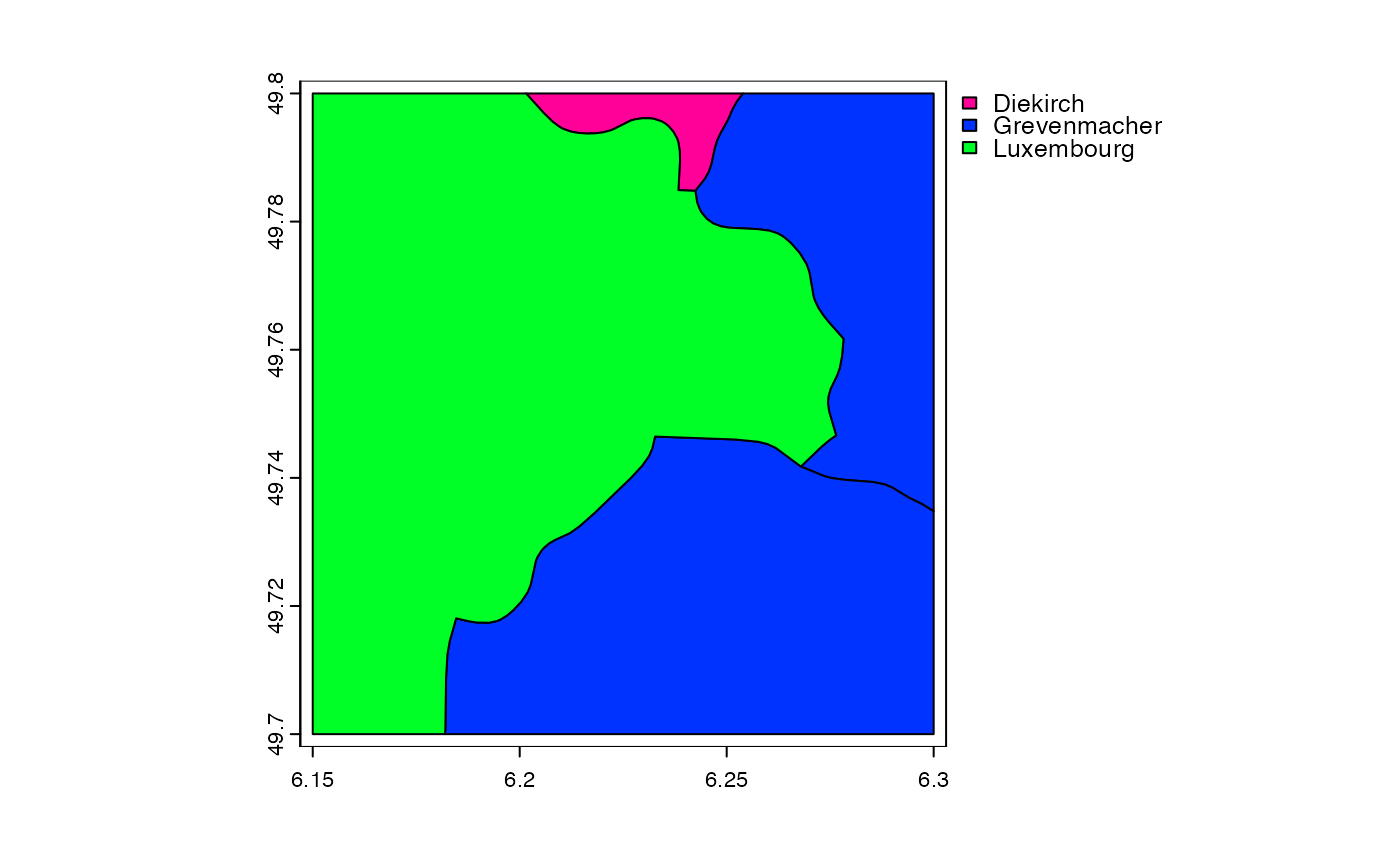
 # crop vector
f <- system.file("ex/lux.shp", package="terra")
v <- vect(f)
e <- ext(6.15, 6.3, 49.7, 49.8)
x <- crop(v, e)
plot(x, "NAME_1")
# crop vector
f <- system.file("ex/lux.shp", package="terra")
v <- vect(f)
e <- ext(6.15, 6.3, 49.7, 49.8)
x <- crop(v, e)
plot(x, "NAME_1")