
Make a map
plot.RdPlot the values of a SpatRaster or SpatVector to make a map.
See points, lines or polys to add a SpatVector to an existing map (or use argument add=TRUE).
There is a separate help file for plotting a SpatGraticule or SpatExtent.
Usage
# S4 method for class 'SpatRaster,numeric'
plot(x, y=1, col, type=NULL, mar=NULL, legend=TRUE, axes=!add, plg=list(), pax=list(),
maxcell=500000, smooth=FALSE, range=NULL, fill_range=FALSE, levels=NULL,
all_levels=FALSE, breaks=NULL, breakby="eqint", fun=NULL, colNA=NULL, alpha=NULL,
sort=FALSE, reverse=FALSE, grid=FALSE, zebra=FALSE, ext=NULL, reset=FALSE,
add=FALSE, buffer=FALSE, background=NULL, box=axes, clip=TRUE, overview=NULL, ...)
# S4 method for class 'SpatRaster,missing'
plot(x, y, main, mar=NULL, nc, nr, maxnl=16, maxcell=500000, add=FALSE,
plg=list(), pax=list(), ...)
# S4 method for class 'SpatRaster,character'
plot(x, y, ...)
# S4 method for class 'SpatVector,character'
plot(x, y, col=NULL, type=NULL, mar=NULL, legend=TRUE, axes=!add, plg=list(), pax=list(),
main="", grid=FALSE, zebra=FALSE, ext=NULL, sort=TRUE, reverse=FALSE, fun=NULL,
colNA=NA, alpha=NULL, nr, nc, add=FALSE, buffer=TRUE, background=NULL,
box=axes, clip=TRUE, ...)
# S4 method for class 'SpatVector,numeric'
plot(x, y, ...)
# S4 method for class 'SpatVector,missing'
plot(x, y, values=NULL, ...)
# S4 method for class 'SpatVectorCollection,missing'
plot(x, y, main, mar=NULL, nc, nr, maxnl=16, col=NULL, ...)
# S4 method for class 'SpatVectorCollection,numeric'
plot(x, y, main, mar=NULL, ext=NULL, ...)Arguments
- x
SpatRaster or SpatVector
- y
missing or positive integer or name indicating the layer(s) to be plotted
- col
character vector to specify the colors to use. The default is
map.pal("viridis", 100). The default can be changed with theterra.paloption. For example:options(terra.pal=terrain.colors(10)). Ifxis aSpatRasterit can also be adata.framewith two columns (value, color) for a "classes" type legend or with three columns (from, to, color) for an "interval" type legend. Ifxis aSpatVectorit can also be adata.framewith two columns (value, color) or a named vector (value=color) for a "classes" type legend. Ifxis a SpatVectorCollection, a list can be provided with colors for each SpatVector- type
character. Type of map/legend. One of "continuous", "classes", or "interval". If not specified, the type is chosen based on the data
- mar
numeric vector of length 4 to set the margins of the plot (to make space for the legend). The default is (3.1, 3.1, 2.1, 7.1) for a single plot with a legend and (3.1, 3.1, 2.1, 2.1) otherwise. The default for a RGB raster is 0. Use
mar=NAto not set the margins- legend
logical or character. If not
FALSEa legend is drawn. The character value can be used to indicate where the legend is to be drawn. For example "topright" or "bottomleft". Useplgfor more refined placement. Not supported for continuous legends (the default for raster data)- axes
logical. Draw axes?
- buffer
logical. If
TRUEthe plotting area is made slightly larger than the extent ofx- background
background color. Default is no color (white)
- box
logical. Should a box be drawn around the map?
- clip
logical. Should the axes be clipped to the extent of
x?- overview
logical. Should "overviews" be used for fast rendering? This can result in much faster plotting of raster files that have overviews (e.g. "COG" format) and are accessed over a http connection. However, these overviews generally show aggregate values, thus reducing the range of the actual values. If
NULL, the argument is set toTRUEfor rasters that are accessed over http andFALSEin other cases- plg
list with parameters for drawing the legend. See the arguments for
legend.A legend can be placed with placed by specifying arguments
xandy. For a continuous legendycan have two values.xcan also be a SpatExtent. Furthermore,xcan have be a keyword such "topleft" and "bottomright" to place the legend at these locations inside the map rectangle. For a continuous legend, only the placement keywords "left", "right", "top", "bottom", "topright", "bottomright" are recognized; and when using these keywords, the legend is placed outside of the map rectangle. The placement of the legend can be altered with argumentnudgethat move the location in the directions specified with one value (x direction) or two values (x, y). For a continuous legend it can also have four values (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). When supplying coordinates, usehoriz=TRUEto get a horizontal legend.Additional parameters for continuous legends include:
digitsinteger. The number of digits to print after the decimal pointsizeto change the height and/or width; the defaults arec(1,1)atto set the location of the tickmarksformatas informatCto format the numbers. For example, you can useformat="g"for scientific notation. The default is"f"tickOne of these partially matched values: "through", "in", "middle", "out", or "none", to choose a tickmark placement/length that is different from the default "throughout".tick.lengthto change the tickmark length (default = 1). Only relevant whentickis "throughout" or "out".tick.col,tick.box.colandtick.lwdto change the appearance of the tickmarkstitle.srtto rotate the legend titletitle.xandtitle.yto place the legend title at specific coordinates
- pax
list with parameters for drawing axes. See the arguments for
axis. Additional parameters include:sidenumeric to indicate for which of the axes to draw a line. Default is1:4(only noticble whenbox=FALSE.ticknumeric to indicate for which of the axes to draw tickmarks. Default is1:2unlesssideis changed, in which case the default is the same assidelabnumeric to indicate for which of the axes to draw labels. Default is1:2unlesssideis changed, in which case the default is the same assidexat/yatnumeric with the values at which tickmarks are to be drawn on the horizontal/vertical axis.xlabs/ylabsthis can either be a logical value specifying whether (numerical) annotations are to be made at the tickmarks, or a character or expression vector of labels to be placed at the tickmarks of the horizontal/vertical axis.retroa logical value that can be set toTRUEto use a sexagesimal notation for the labels (degrees/minutes/hemisphere) instead of the standard decimal notation. For longitude/latitude data only. Seegraticulefor projected data.
- maxcell
positive integer. Maximum number of cells to use for the plot
- smooth
logical. If
TRUEthe cell values are smoothed (only if a continuous legend is used)- range
numeric. minimum and maximum values to be used for the continuous legend. You can use
NAfor one of these to only set the minimum or maximum value- fill_range
logical. If
TRUE, values outside ofrangeget the colors of the extreme values; otherwise they get colored asNA- levels
character. labels for the legend when
type="classes"- all_levels
logical. If
TRUE, the legend shows all levels of a categorical raster, even if they are not present in the data- breaks
numeric. Either a single number to indicate the number of breaks desired, or the actual breaks. When providing this argument, the default legend becomes "interval"
- breakby
character or function. Either "eqint" for equal interval breaks, "cases" for equal quantile breaks. If a function is supplied, it should take a single argument (a vector of values) and create groups
- fun
function to be called after plotting each SpatRaster layer to add something to each map (such as text, legend, lines). For example, with SpatVector
v, you could dofun=function() lines(v). The function may have one argument, representing the layer that is plotted (1 to the number of layers)- colNA
character. color for the NA values
- alpha
Either a single numeric between 0 and 1 to set the transparency for all colors (0 is transparent, 1 is opaque) or a SpatRaster with values between 0 and 1 to set the transparency by cell. To set the transparency for a given color, set it to the colors directly
- sort
logical. If
TRUElegends with categorical values are sorted. Ifxis aSpatVectoryou can also supply a vector of the unique values, in the order in which you want them to appear in the legend- reverse
logical. If
TRUE, the legend order is reversed- grid
logical. If
TRUEgrid lines are drawn. Their properties such as type and color can be set with thepaxargument. The grid is drawn first such that it is covered byx. Seeadd_gridto add grid lines on top of the map- zebra
logical. If
TRUEa "zebra-box" is added to the axes (ignored whenadd=TRUE). The width of the zebra-box can be set with additional argumentzebra.cex. The colors can be changed with additional argumentzebra.col- nc
positive integer. Optional. The number of columns to divide the plotting device in (when plotting multiple layers)
- nr
positive integer. Optional. The number of rows to divide the plotting device in (when plotting multiple layers)
- main
character. Main plot titles (one for each layer to be plotted). You can use arguments
cex.main,font.main,col.mainto change the appearance; andloc.mainto change the location of the main title (either two coordinates, or a character value such as "topleft"). You can also usesub=""for a subtitle. Seetitle- maxnl
positive integer. Maximum number of layers to plot (for a multi-layer object).
- add
logical. If
TRUEadd the object to the current plot- ext
SpatExtent. Can be use instead of xlim and ylim to set the extent of the plot
- reset
logical. If
TRUEthe margins (see argumentmar) are reset to what they were before calling plot; doing so may affect the display of additional objects that are added to the map (e.g. withlines)- values
Either a vector with values to be used for plotting or a two-column data.frame, where the first column matches a variable in
xand the second column has the values to be plotted- ...
arguments passed to
plot("SpatRaster", "numeric")and additional graphical arguments
Examples
## SpatRaster
f <- system.file("ex/elev.tif", package="terra")
r <- rast(f)
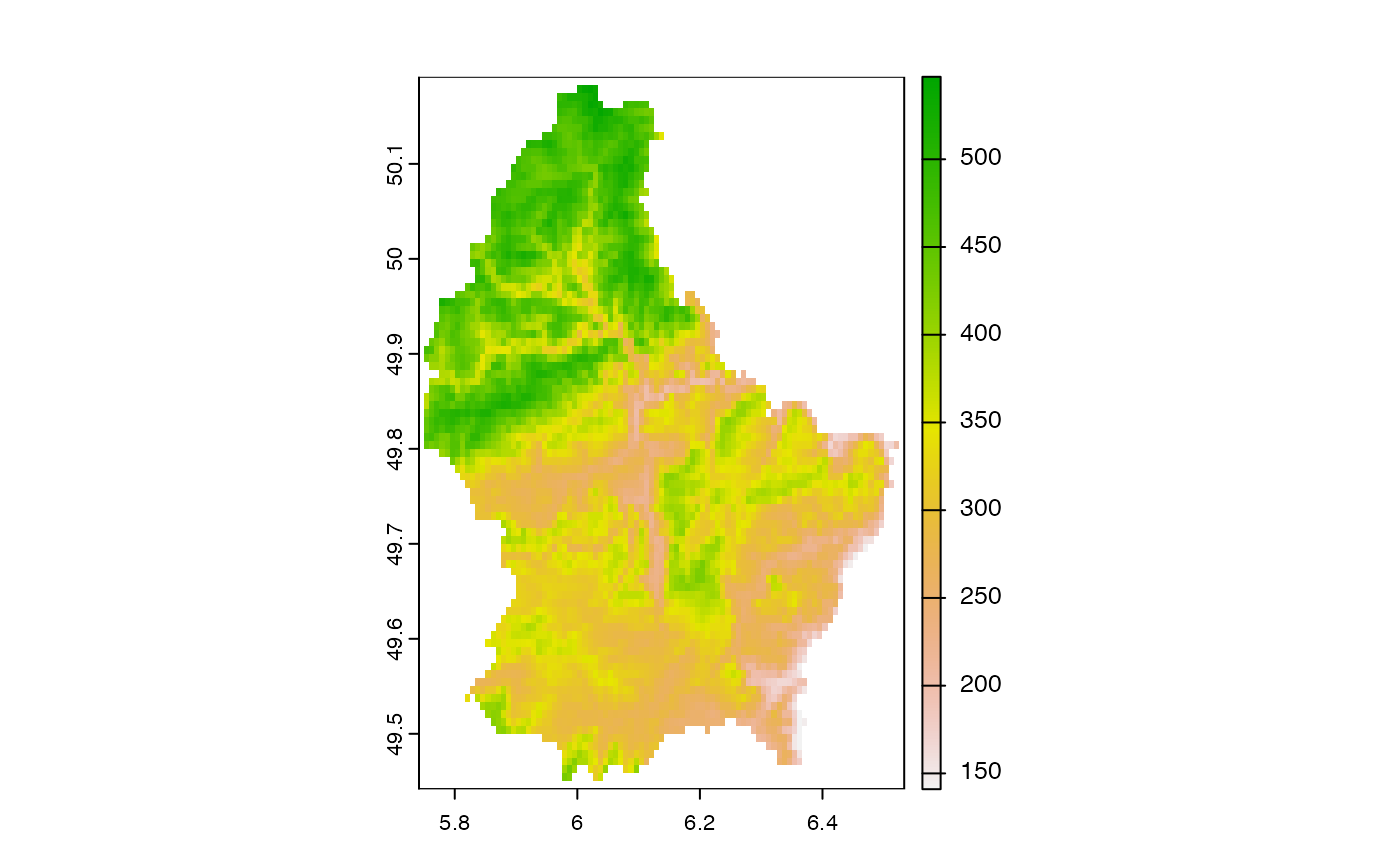
plot(r)
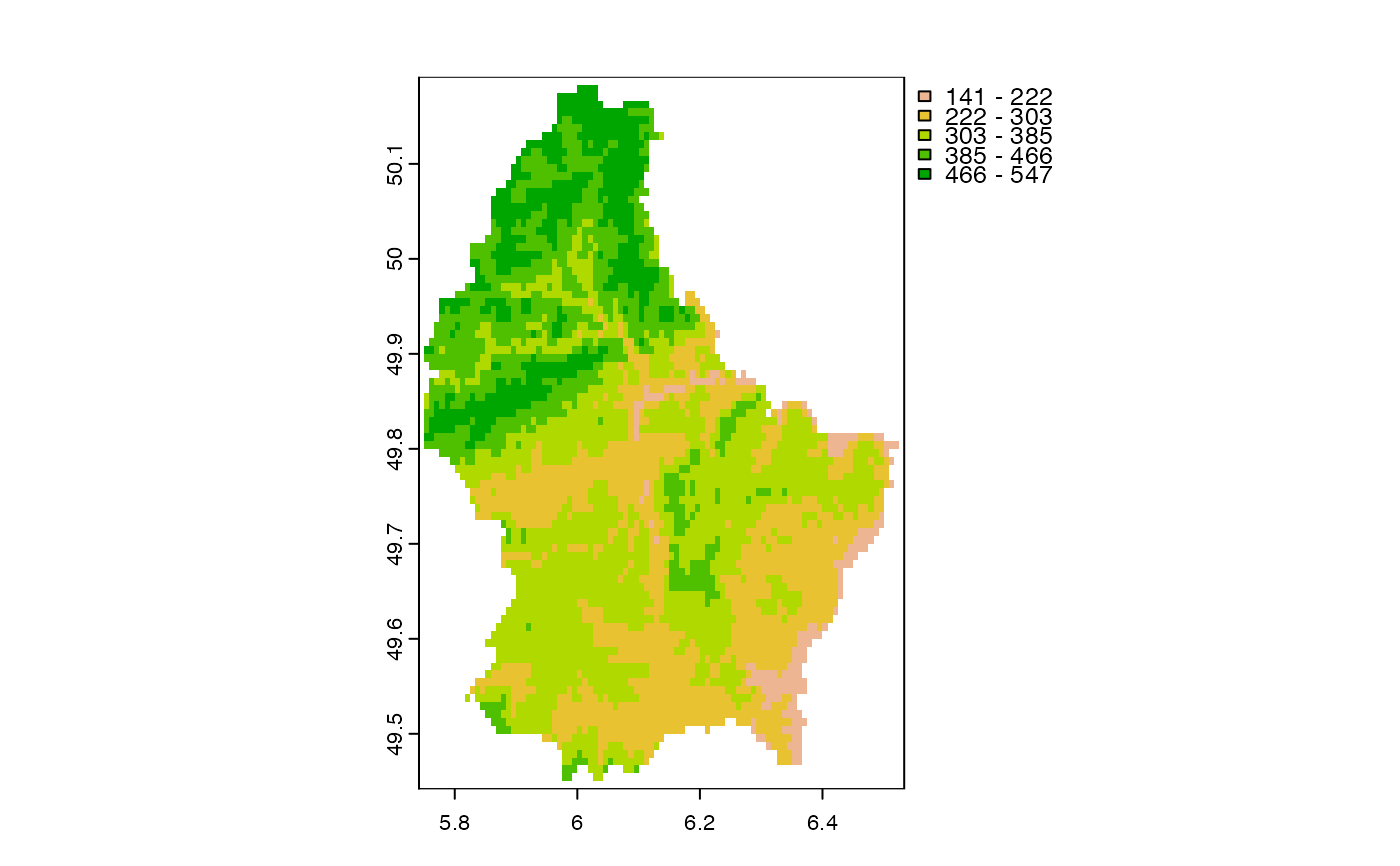
 plot(r, type="interval")
plot(r, type="interval")
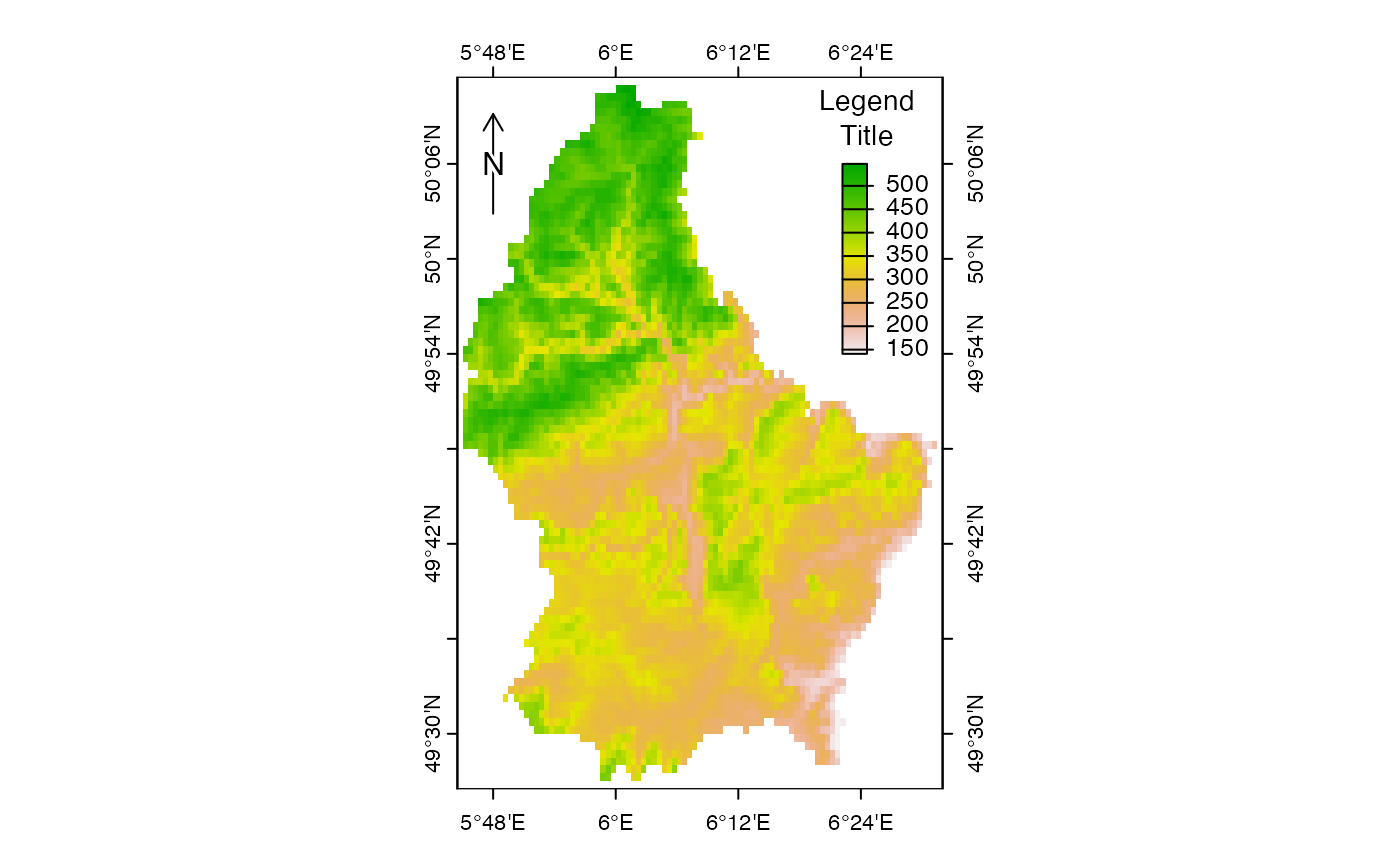
 plot(r, plg=list(x=6.35, y = c(49.9, 50.1), title="Legend\nTitle", title.cex=0.9),
pax=list(side=1:4, retro=FALSE))
north(cbind(5.8, 50.1))
plot(r, plg=list(x=6.35, y = c(49.9, 50.1), title="Legend\nTitle", title.cex=0.9),
pax=list(side=1:4, retro=FALSE))
north(cbind(5.8, 50.1))
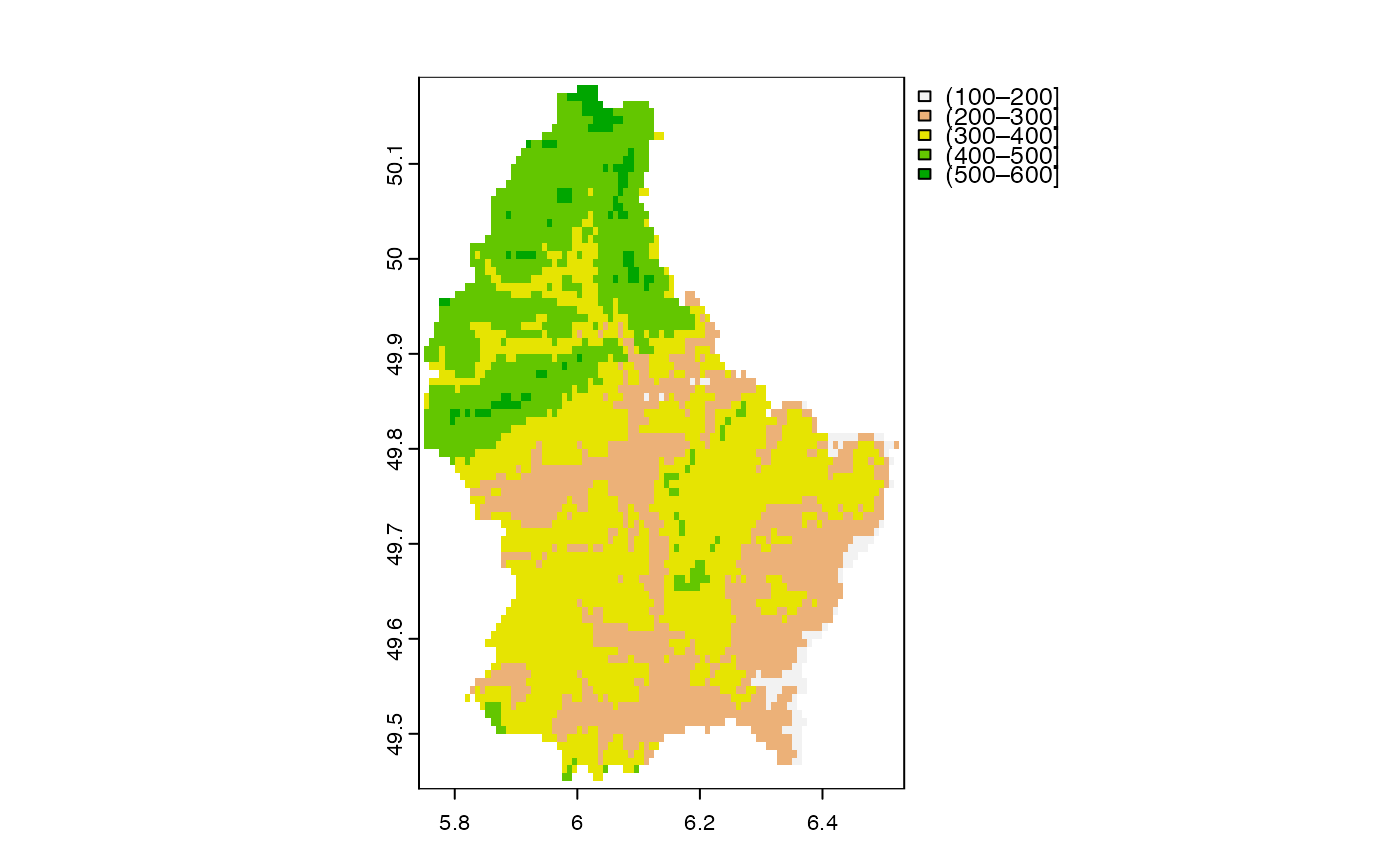
 d <- classify(r, c(100,200,300,400,500,600))
plot(d)
d <- classify(r, c(100,200,300,400,500,600))
plot(d)
 plot(d, type="interval", breaks=1:5)
plot(d, type="interval", breaks=1:5)
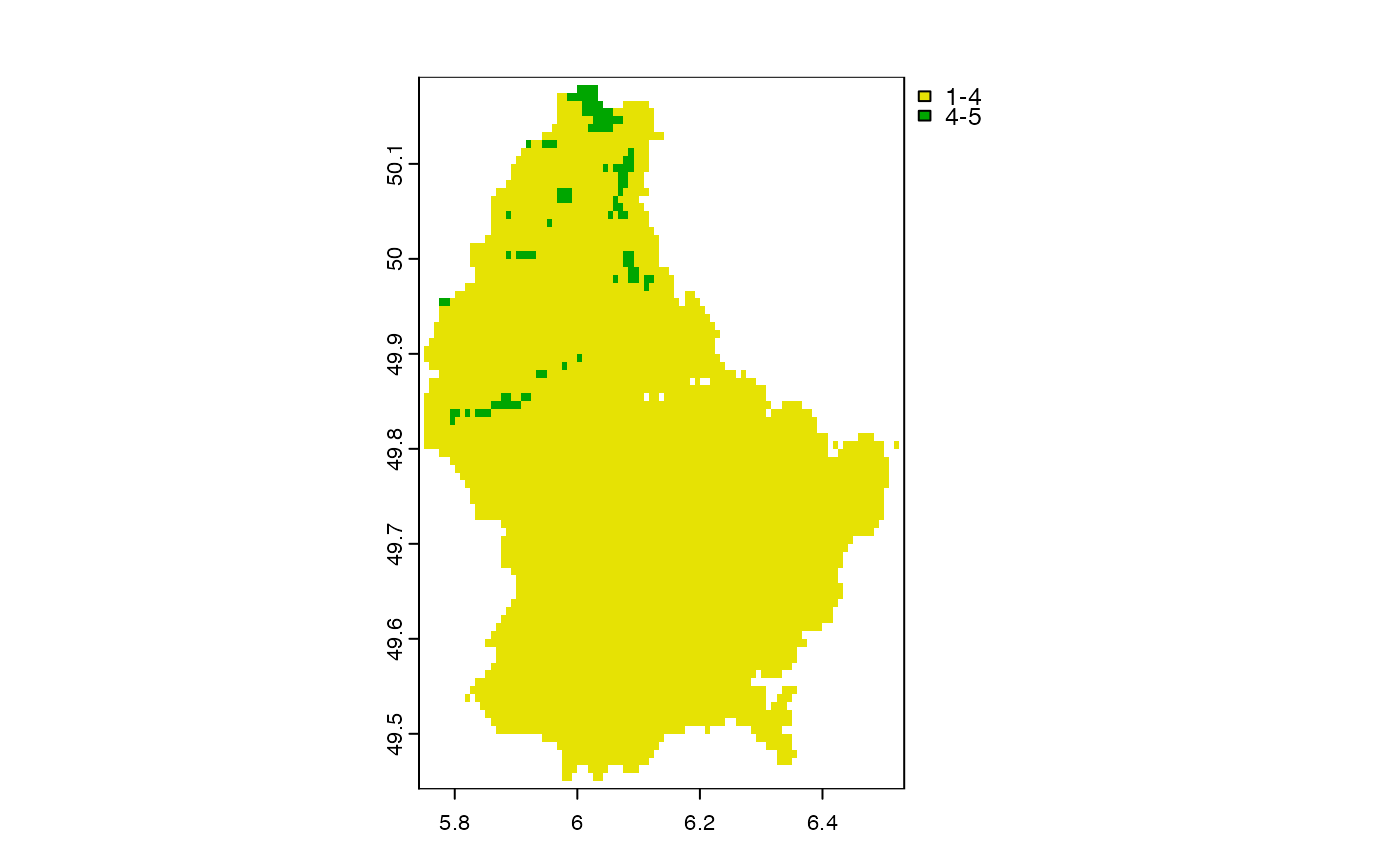
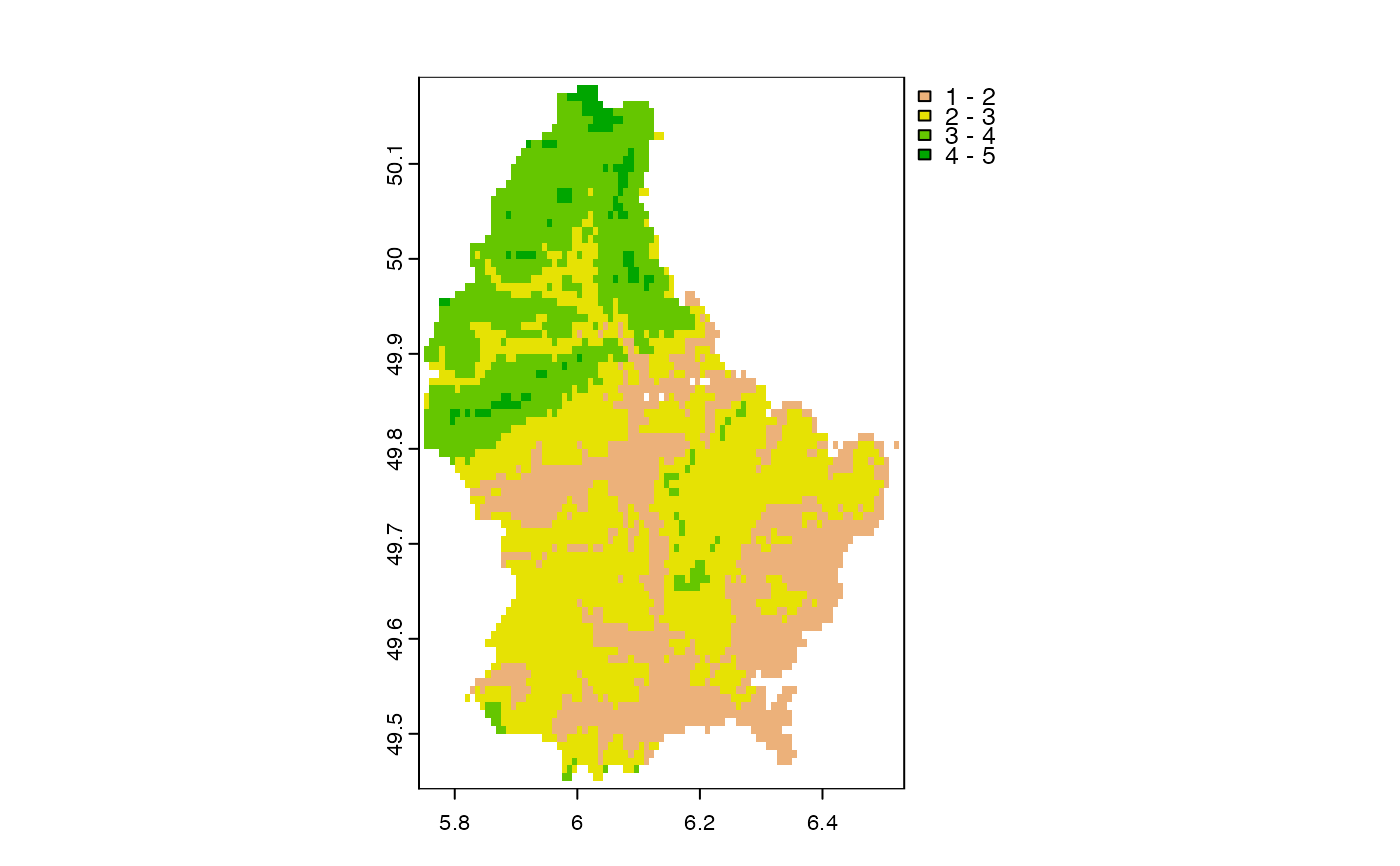 plot(d, type="interval", breaks=c(1,4,5), plg=list(legend=c("1-4", "4-5")))
plot(d, type="interval", breaks=c(1,4,5), plg=list(legend=c("1-4", "4-5")))
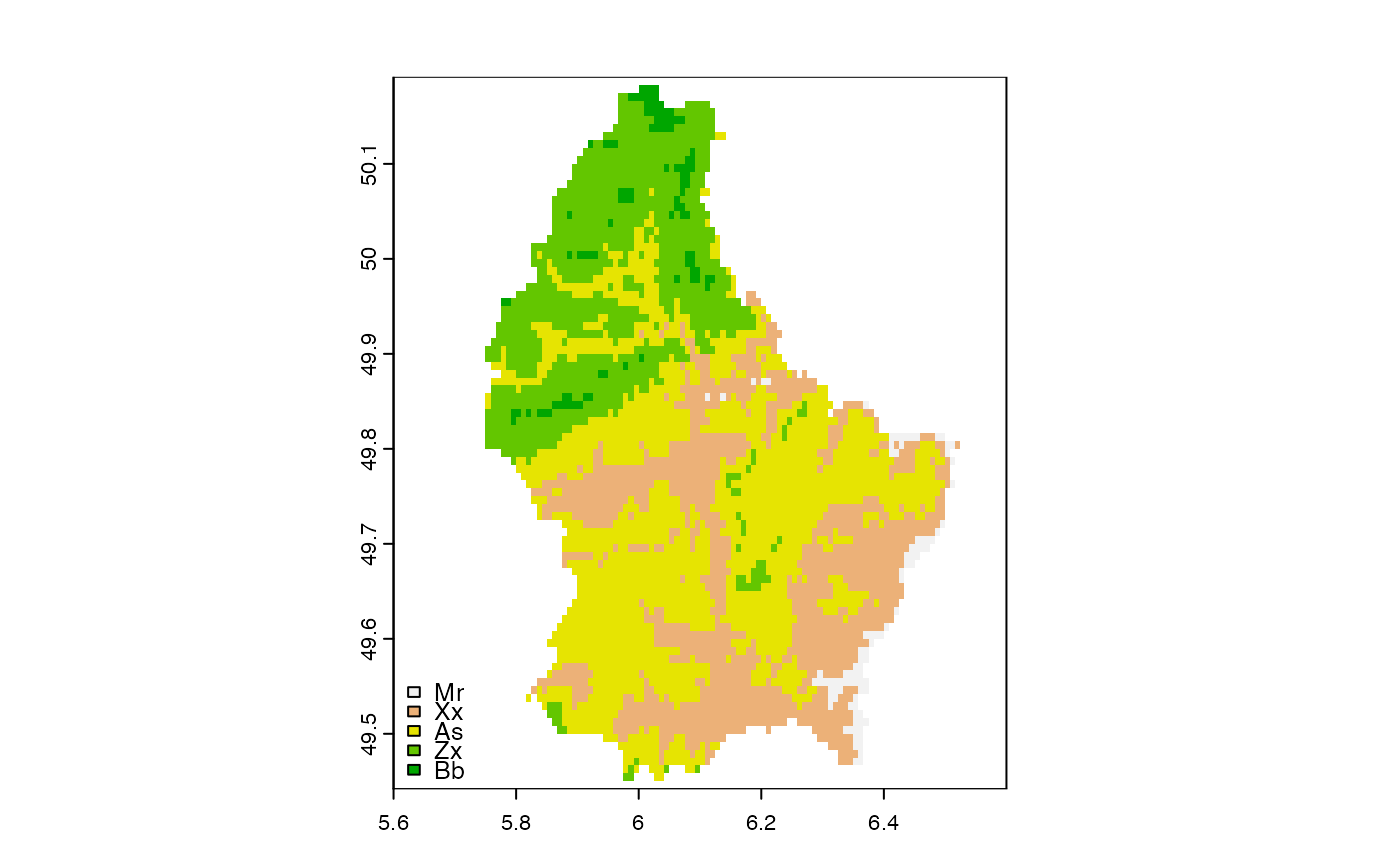
 plot(d, type="classes", xlim=c(5.6, 6.6),
plg=list(legend=c("Mr", "Xx", "As", "Zx", "Bb"), x="bottomleft"))
plot(d, type="classes", xlim=c(5.6, 6.6),
plg=list(legend=c("Mr", "Xx", "As", "Zx", "Bb"), x="bottomleft"))
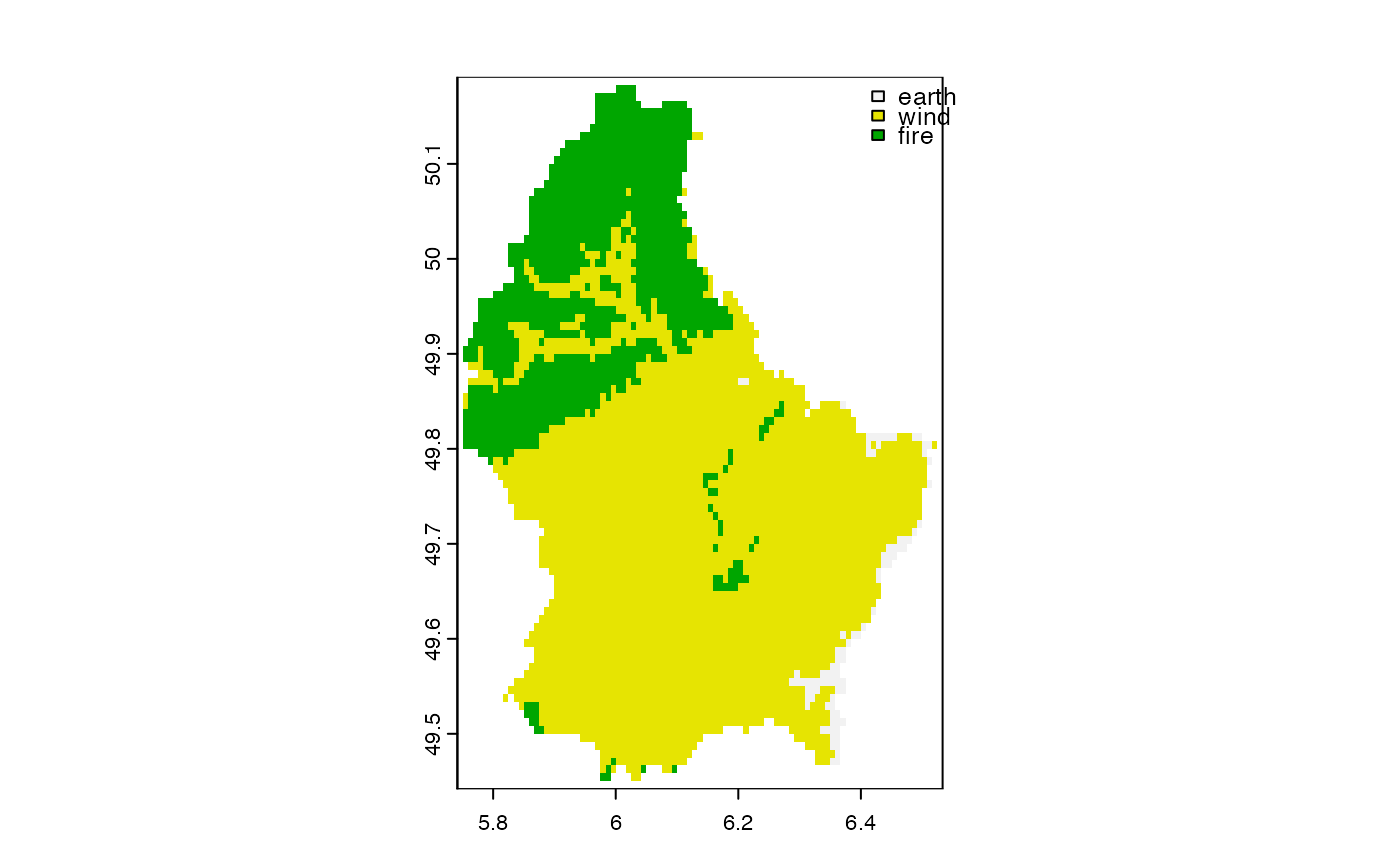
 x <- trunc(r/200)
levels(x) <- data.frame(id=0:2, element=c("earth", "wind", "fire"))
plot(x, plg=list(x="topright"),mar=c(2,2,2,2))
x <- trunc(r/200)
levels(x) <- data.frame(id=0:2, element=c("earth", "wind", "fire"))
plot(x, plg=list(x="topright"),mar=c(2,2,2,2))
 oldpar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
# two plots with the same legend
dev.new(width=6, height=4, noRStudioGD = TRUE)
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
plot(r, range=c(50,600), mar=c(1,1,1,4))
plot(r/2, range=c(50,600), mar=c(1,1,1,4))
# as we only need one legend (also see the "panel" method):
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
plot(r, range=c(50,600), mar=c(2, 2, 2, 2), plg=list(size=0.9, cex=.8),
pax=list(side=1:2, cex.axis=.6), box=FALSE)
#text(182500, 335000, "Two maps, one plot", xpd=NA)
plot(r/2, range=c(50,600), mar=c(2, 2, 2, 2), legend=FALSE,
pax=list(side=c(1,4), cex.axis=.6), box=FALSE)
par(oldpar)
# multi-layer with RGB
s <- rast(system.file("ex/logo.tif", package="terra"))
s
#> class : SpatRaster
#> size : 77, 101, 3 (nrow, ncol, nlyr)
#> resolution : 1, 1 (x, y)
#> extent : 0, 101, 0, 77 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
#> coord. ref. : Cartesian (Meter)
#> source : logo.tif
#> colors RGB : 1, 2, 3
#> names : red, green, blue
#> min values : 0, 0, 0
#> max values : 255, 255, 255
plot(s)
# remove RGB
plot(s*1)
# or use layers
plot(s, 1)
plot(s, 1:3)
# fix legend by linking values and colors
x = rast(nrows = 2, ncols = 2, vals=1)
y = rast(nrows = 2, ncols = 2, vals=c(1,2,2,1))
cols = data.frame(id=1:2, col=c("red", "blue"))
plot(c(x,y), col=cols)
r = rast(nrows=10, ncols=10, vals=1:100)
dr = data.frame(from=c(5,33,66,150), to=c(33, 66, 95,200), col=rainbow(4))
plot(r, col=dr)
### SpatVector
f <- system.file("ex/lux.shp", package="terra")
v <- vect(f)
plot(v)
plot(v, "NAME_2", col=rainbow(12), border=c("gray", "blue"), lwd=3, zebra=TRUE)
plot(v, 2, pax=list(side=1:2), plg=list(x=6.16, y=50.17, cex=.8), xlim=c(5.7, 6.7))
plot(v, 4, pax=list(side=1:2), plg=list(x=6.2, y=50.2, ncol=2), main="", box=FALSE)
plot(v, 1, plg=list(x=5.8, y=49.37, horiz=TRUE, cex=1.1), main="", mar=c(5,2,0.5,0.5))
plot(v, density=1:12, angle=seq(18, 360, 20), col=rainbow(12))
plot(v, "AREA", type="interval", breaks=3, mar=c(3.1, 3.1, 2.1, 3.1),
plg=list(x="topright"), main="")
plot(v, "AREA", type="interval", breaks=c(0,200,250,350),
mar=c(2,2,2,2), xlim=c(5.7, 6.75),
plg=list(legend=c("<200", "200-250", ">250"), cex=1, bty="o",
x=6.3, y=50.15, box.lwd=2, bg="light yellow", title="My legend"))
oldpar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
# two plots with the same legend
dev.new(width=6, height=4, noRStudioGD = TRUE)
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
plot(r, range=c(50,600), mar=c(1,1,1,4))
plot(r/2, range=c(50,600), mar=c(1,1,1,4))
# as we only need one legend (also see the "panel" method):
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
plot(r, range=c(50,600), mar=c(2, 2, 2, 2), plg=list(size=0.9, cex=.8),
pax=list(side=1:2, cex.axis=.6), box=FALSE)
#text(182500, 335000, "Two maps, one plot", xpd=NA)
plot(r/2, range=c(50,600), mar=c(2, 2, 2, 2), legend=FALSE,
pax=list(side=c(1,4), cex.axis=.6), box=FALSE)
par(oldpar)
# multi-layer with RGB
s <- rast(system.file("ex/logo.tif", package="terra"))
s
#> class : SpatRaster
#> size : 77, 101, 3 (nrow, ncol, nlyr)
#> resolution : 1, 1 (x, y)
#> extent : 0, 101, 0, 77 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
#> coord. ref. : Cartesian (Meter)
#> source : logo.tif
#> colors RGB : 1, 2, 3
#> names : red, green, blue
#> min values : 0, 0, 0
#> max values : 255, 255, 255
plot(s)
# remove RGB
plot(s*1)
# or use layers
plot(s, 1)
plot(s, 1:3)
# fix legend by linking values and colors
x = rast(nrows = 2, ncols = 2, vals=1)
y = rast(nrows = 2, ncols = 2, vals=c(1,2,2,1))
cols = data.frame(id=1:2, col=c("red", "blue"))
plot(c(x,y), col=cols)
r = rast(nrows=10, ncols=10, vals=1:100)
dr = data.frame(from=c(5,33,66,150), to=c(33, 66, 95,200), col=rainbow(4))
plot(r, col=dr)
### SpatVector
f <- system.file("ex/lux.shp", package="terra")
v <- vect(f)
plot(v)
plot(v, "NAME_2", col=rainbow(12), border=c("gray", "blue"), lwd=3, zebra=TRUE)
plot(v, 2, pax=list(side=1:2), plg=list(x=6.16, y=50.17, cex=.8), xlim=c(5.7, 6.7))
plot(v, 4, pax=list(side=1:2), plg=list(x=6.2, y=50.2, ncol=2), main="", box=FALSE)
plot(v, 1, plg=list(x=5.8, y=49.37, horiz=TRUE, cex=1.1), main="", mar=c(5,2,0.5,0.5))
plot(v, density=1:12, angle=seq(18, 360, 20), col=rainbow(12))
plot(v, "AREA", type="interval", breaks=3, mar=c(3.1, 3.1, 2.1, 3.1),
plg=list(x="topright"), main="")
plot(v, "AREA", type="interval", breaks=c(0,200,250,350),
mar=c(2,2,2,2), xlim=c(5.7, 6.75),
plg=list(legend=c("<200", "200-250", ">250"), cex=1, bty="o",
x=6.3, y=50.15, box.lwd=2, bg="light yellow", title="My legend"))