Categorical rasters
factors.RdA SpatRaster layer can represent a categorical variable (factor). Like factors, SpatRaster categories are stored as integers that have an associated label.
The categories can be inspected with levels and cats. They are represented by a data.frame that must have two or more columns, the first one identifying the (integer) cell values and the other column(s) providing the category labels.
If there are multiple columns with categories, you can set the "active" category to choose the one you want to use.
cats returns the entire data.frame, whereas levels only return two columns: the index and the active category.
To set categories for the first layer of a SpatRaster, you can provide levels<- with a data.frame or a list with a data.frame. To set categories for multiple layers you can provide levels<- with a list with one element (that either has a data.frame or is NULL) for each layer. Use categories to set the categories for a specific layer or specific layers.
droplevels removes categories that are not used (declared but not present as values in the raster) if levels=NULL.
simplifyLevels combines duplicate levels into one.
addCats adds additional categories to a layer that already is categorical. It adds new variables, not new levels of an existing categorical variable.
combineLevels combines the levels of all layers of x and sets them to all layers. That fails if there are labeling conflicts between layers
Usage
# S4 method for class 'SpatRaster'
levels(x)
# S4 method for class 'SpatRaster'
levels(x) <- value
# S4 method for class 'SpatRaster'
cats(x, layer)
# S4 method for class 'SpatRaster'
categories(x, layer=1, value, active=1, ...)
# S4 method for class 'SpatRaster'
droplevels(x, level=NULL, layer=1)
# S4 method for class 'SpatRaster'
simplifyLevels(x, filename="", overwrite=FALSE, ...)
# S4 method for class 'SpatRaster'
addCats(x, value, merge=FALSE, layer=1)
combineLevels(x, assign=TRUE)Arguments
- x
SpatRaster
- layer
the layer name or number (positive integer); or 0 for all layers
- value
a data.frame (ID, category) that define the categories. Or
NULLto remove them- active
positive integer, indicating the column in
valueto be used as the active category (zero based to skip the first column with the cell values; that is 1 is the second column invalue)- level
the categories to remove for the layer specified with
layer- merge
logical. If
TRUE, the categories are combined withmergeusing the first column ofvalueas ID. IfFALSEthe categories are combined withcbind- assign
logical. Assign the combined levels to all layers of
x? IfFALSE, the levels are returned- filename
character. Output filename
- overwrite
logical. If
TRUE,filenameis overwritten- ...
additional arguments for writing files as in
writeRaster
Examples
set.seed(0)
r <- rast(nrows=10, ncols=10)
values(r) <- sample(3, ncell(r), replace=TRUE)
is.factor(r)
#> [1] FALSE
cls <- data.frame(id=1:3, cover=c("forest", "water", "urban"))
levels(r) <- cls
is.factor(r)
#> [1] TRUE
r
#> class : SpatRaster
#> size : 10, 10, 1 (nrow, ncol, nlyr)
#> resolution : 36, 18 (x, y)
#> extent : -180, 180, -90, 90 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
#> coord. ref. : lon/lat WGS 84 (CRS84) (OGC:CRS84)
#> source(s) : memory
#> categories : cover
#> name : cover
#> min value : forest
#> max value : urban
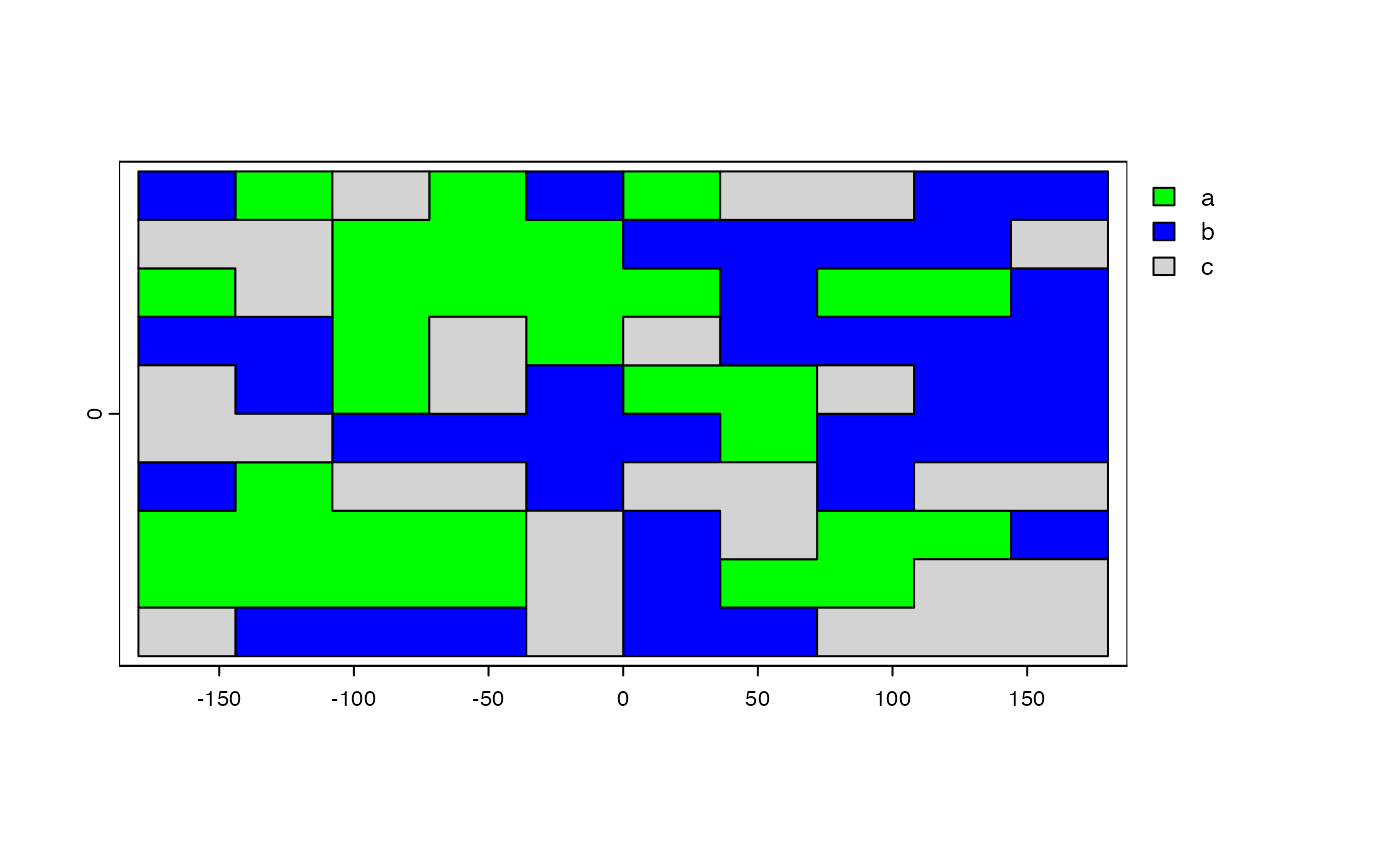
plot(r, col=c("green", "blue", "light gray"))
text(r, digits=3, cex=.75, halo=TRUE)
 levels(r) <- data.frame(id=1:3, cover=c("forest", "water", "forest"))
levels(simplifyLevels(r))
#> [[1]]
#> id cover
#> 1 1 forest
#> 2 2 water
#>
# raster starts at 3
x <- r + 2
is.factor(x)
#> [1] FALSE
# Multiple categories
d <- data.frame(id=3:5, cover=cls[,2], letters=letters[1:3], value=10:12)
levels(x) <- d
x
#> class : SpatRaster
#> size : 10, 10, 1 (nrow, ncol, nlyr)
#> resolution : 36, 18 (x, y)
#> extent : -180, 180, -90, 90 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
#> coord. ref. : lon/lat WGS 84 (CRS84) (OGC:CRS84)
#> source(s) : memory
#> categories : cover, letters, value
#> name : cover
#> min value : forest
#> max value : urban
# get current index
activeCat(x)
#> [1] 1
# set index
activeCat(x) <- 3
activeCat(x)
#> [1] 3
activeCat(x) <- "letters"
plot(x, col=c("green", "blue", "light gray"))
text(x, digits=3, cex=.75, halo=TRUE)
levels(r) <- data.frame(id=1:3, cover=c("forest", "water", "forest"))
levels(simplifyLevels(r))
#> [[1]]
#> id cover
#> 1 1 forest
#> 2 2 water
#>
# raster starts at 3
x <- r + 2
is.factor(x)
#> [1] FALSE
# Multiple categories
d <- data.frame(id=3:5, cover=cls[,2], letters=letters[1:3], value=10:12)
levels(x) <- d
x
#> class : SpatRaster
#> size : 10, 10, 1 (nrow, ncol, nlyr)
#> resolution : 36, 18 (x, y)
#> extent : -180, 180, -90, 90 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
#> coord. ref. : lon/lat WGS 84 (CRS84) (OGC:CRS84)
#> source(s) : memory
#> categories : cover, letters, value
#> name : cover
#> min value : forest
#> max value : urban
# get current index
activeCat(x)
#> [1] 1
# set index
activeCat(x) <- 3
activeCat(x)
#> [1] 3
activeCat(x) <- "letters"
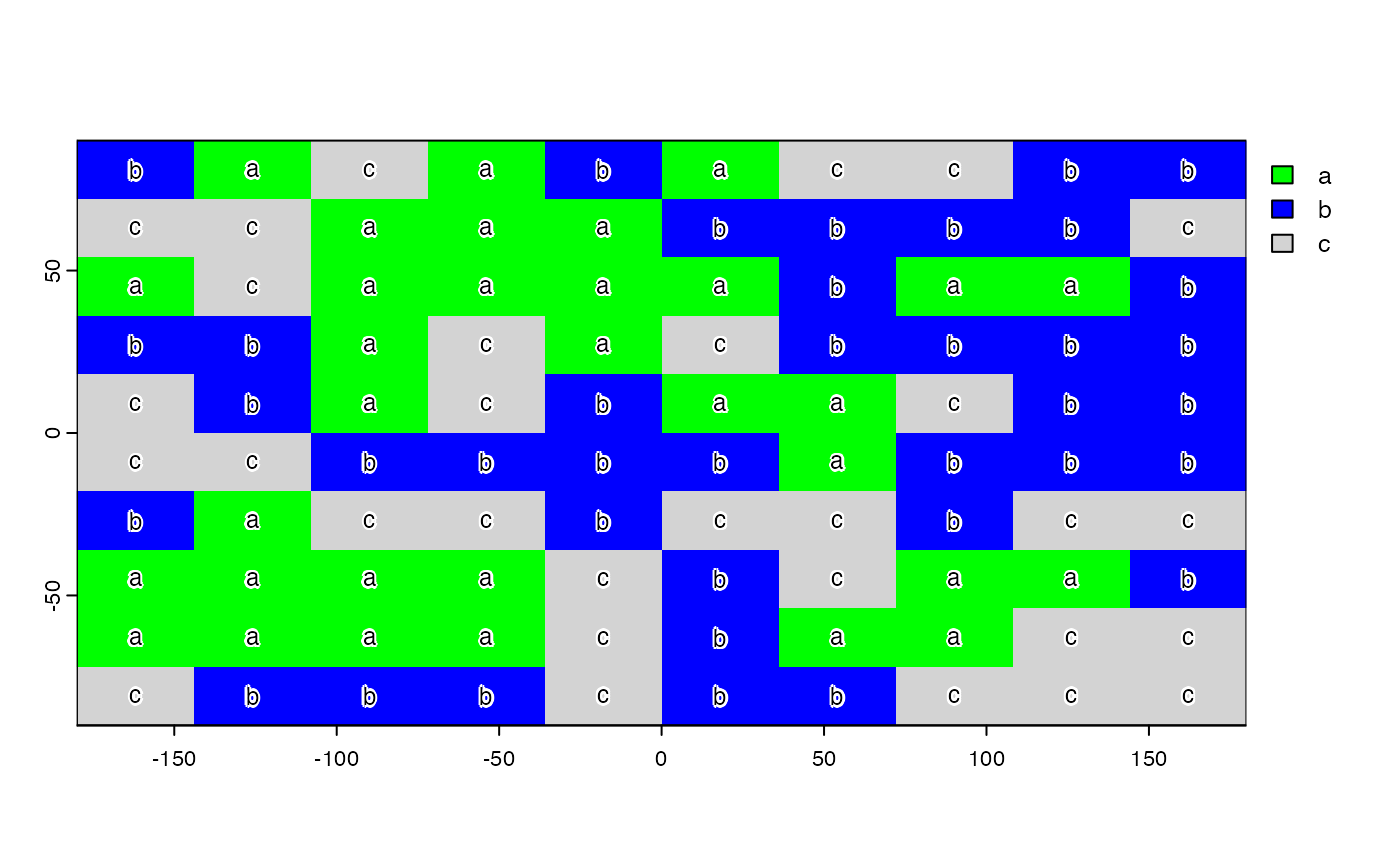
plot(x, col=c("green", "blue", "light gray"))
text(x, digits=3, cex=.75, halo=TRUE)
 r <- as.numeric(x)
r
#> class : SpatRaster
#> size : 10, 10, 1 (nrow, ncol, nlyr)
#> resolution : 36, 18 (x, y)
#> extent : -180, 180, -90, 90 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
#> coord. ref. : lon/lat WGS 84 (CRS84) (OGC:CRS84)
#> source(s) : memory
#> name : cover
#> min value : 1
#> max value : 3
p <- as.polygons(x)
plot(p, "letters", col=c("green", "blue", "light gray"))
r <- as.numeric(x)
r
#> class : SpatRaster
#> size : 10, 10, 1 (nrow, ncol, nlyr)
#> resolution : 36, 18 (x, y)
#> extent : -180, 180, -90, 90 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
#> coord. ref. : lon/lat WGS 84 (CRS84) (OGC:CRS84)
#> source(s) : memory
#> name : cover
#> min value : 1
#> max value : 3
p <- as.polygons(x)
plot(p, "letters", col=c("green", "blue", "light gray"))